PCIE驱动设备文件的创建与操作
2024-09-14
250
1
一、前言
在 Linux 中一切皆为文件,驱动加载成功以后会在“/dev”目录下生成一个相应的文件,应用程序通过对这个名为“/dev/xxx” (xxx 是具体的驱动文件名字)的文件进行相应的操作即可实现对硬件的操作。
二、创建设备文件
PCIe设备属于字符设备,我们按如下步骤创建一个字符设备:
/* 1、Request device number */
ret = alloc_chrdev_region(&hello_pci_info.dev_id, 0, 1, "hello_pcie");
/* 2、Initial char_dev */
hello_pci_info.cdev.owner = THIS_MODULE;
cdev_init(&hello_pci_info.char_dev, &hello_pci_fops);
/* 3、add char_dev */
cdev_add(&hello_pci_info.char_dev, hello_pci_info.dev_id, 1);
/* 4、create class */
hello_pci_info.class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "hello_pcie");
if (IS_ERR(hello_pci_info.class)) {
return PTR_ERR(hello_pci_info.class);
}
/* 5、create device */
hello_pci_info.device = device_create(hello_pci_info.class, NULL, hello_pci_info.dev_id, NULL, "hello_pcie");
if (IS_ERR(newchrled.device)) {
return PTR_ERR(newchrled.device);
}
其中需要定义一个设备文件操作函数结构体,可以暂时定义为如下所示:
/* device file operations function */
static struct file_operations hello_pcie_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
};
将上述创建一个字符设备的操作加在hello_pci_init函数里,同时hello_pci_exit添加对应的卸载操作:
static void __exit hello_pci_exit(void)
{
if(hello_pci_info.dev != NULL) {
cdev_del(&hello_pci_info.char_dev); /* del cdev */
unregister_chrdev_region(hello_pci_info.dev_id, 1); /* unregister device number */
device_destroy(hello_pci_info.class, hello_pci_info.dev_id);
class_destroy(hello_pci_info.class);
}
pci_unregister_driver(&hello_pci_driver);
}
然后编译加载驱动,便可以看到在/dev下有我们创建的hello_pcie设备了: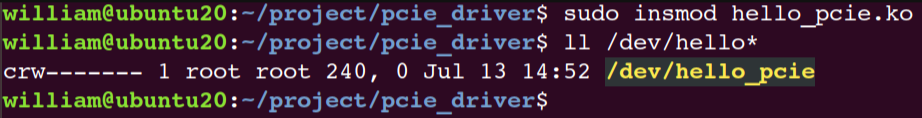
三、添加文件操作函数
如下所示,添加文件的open,close,write,read函数:
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/pci.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/errno.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#define HELLO_PCI_DEVICE_ID 0x11e8
#define HELLO_PCI_VENDOR_ID 0x1234
#define HELLO_PCI_REVISION_ID 0x10
static struct pci_device_id ids[] = {
{ PCI_DEVICE(HELLO_PCI_VENDOR_ID, HELLO_PCI_DEVICE_ID), },
{ 0 , }
};
static struct hello_pci_info_t {
dev_t dev_id;
struct cdev char_dev;
struct class *class;
struct device *device;
struct pci_dev *dev;
void __iomem *address_bar0;
atomic_t compute_running;
wait_queue_head_t r_wait;
} hello_pci_info;
MODULE_DEVICE_TABLE(pci, ids);
static irqreturn_t hello_pci_irq_handler(int irq, void *dev_info)
{
struct hello_pci_info_t *_pci_info = dev_info;
uint32_t irq_status;
// get irq_stutas
irq_status = *((uint32_t *)(_pci_info->address_bar0 + 0x24));
printk("hello_pcie: get irq status: 0x%0x\n", irq_status);
// clean irq
*((uint32_t *)(_pci_info->address_bar0 + 0x64)) = irq_status;
// get irq_stutas
irq_status = *((uint32_t *)(_pci_info->address_bar0 + 0x24));
if(irq_status == 0x00){
printk("hello_pcie: receive irq and clean success. \n");
}else{
printk("hello_pcie: receive irq but clean failed !!! \n");
return IRQ_NONE;
}
atomic_set(&(_pci_info->compute_running), 0);
wake_up_interruptible(&(_pci_info->r_wait));
return IRQ_HANDLED;
}
/*
* @description : 打开设备
* @param - inode : 传递给驱动的inode
* @param - file : 设备文件,file结构体有个叫做private_data的成员变量
* 一般在open的时候将private_data指向设备结构体。
* @return : 0 成功;其他 失败
*/
static int hello_pcie_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
printk("hello_pcie: open dev file.\n");
init_waitqueue_head(&hello_pci_info.r_wait);
return 0;
}
/*
* @description : 关闭/释放设备
* @param - file : 要关闭的设备文件(文件描述符)
* @return : 0 成功;其他 失败
*/
static int hello_pcie_close(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
printk("hello_pcie: close dev file.\n");
return 0;
}
/*
* @description : 向设备写数据
* @param - filp : 设备文件,表示打开的文件描述符
* @param - buf : 要写给设备写入的数据
* @param - cnt : 要写入的数据长度
* @param - offt : 相对于文件首地址的偏移
* @return : 写入的字节数,如果为负值,表示写入失败
*/
static ssize_t hello_pcie_write(struct file *filp, const char __user *buf, size_t cnt, loff_t *offt)
{
int retvalue;
unsigned char databuf[4] = {0, 0, 0, 0};
uint32_t compute_value;
retvalue = copy_from_user(databuf, buf, cnt);
if(retvalue < 0) {
printk("hello_pcie: write failed!\n");
return -EFAULT;
}
atomic_set(&hello_pci_info.compute_running, 1);
compute_value = ((databuf[0]) | (databuf[1]<<8) | (databuf[2]<<16) | (databuf[3]<<24));
*((uint32_t *)(hello_pci_info.address_bar0 + 0x08)) = compute_value;
return 0;
}
/*
* @description : 从设备读取数据
* @param – filp : 要打开的设备文件(文件描述符)
* @param – buf : 返回给用户空间的数据缓冲区
* @param – cnt : 要读取的数据长度
* @param – offt : 相对于文件首地址的偏移
* @return : 读取的字节数,如果为负值,表示读取失败
*/
static ssize_t hello_pcie_read(struct file *filp, char __user *buf, size_t cnt, loff_t *offt)
{
int ret;
uint32_t compute_result = 0;
/* 加入等待队列,当有按键按下或松开动作发生时,才会被唤醒 */
ret = wait_event_interruptible(hello_pci_info.r_wait, 0 == atomic_read(&hello_pci_info.compute_running));
if(ret)
return ret;
compute_result = *((uint32_t *)(hello_pci_info.address_bar0 + 0x08));
printk("hello_pcie: get compute_result: %0d\n", compute_result);
/* 将按键状态信息发送给应用程序 */
ret = copy_to_user(buf, &compute_result, sizeof(int));
return ret;
}
/* device file operations function */
static struct file_operations hello_pcie_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.open = hello_pcie_open,
.release = hello_pcie_close,
.read = hello_pcie_read,
.write = hello_pcie_write,
};
static int hello_pcie_probe(struct pci_dev *dev, const struct pci_device_id *id)
{
int bar = 0;
int ret;
resource_size_t len;
ret = pci_enable_device(dev);
if(ret) {
return ret;
}
len = pci_resource_len(dev, bar);
hello_pci_info.address_bar0 = pci_iomap(dev, bar, len);
hello_pci_info.dev = dev;
// register interrupt
ret = request_irq(dev->irq, hello_pci_irq_handler, IRQF_SHARED, "hello_pci", &hello_pci_info);
if(ret) {
printk("request IRQ failed.\n");
return ret;
}
// enable irq for finishing factorial computation
*((uint32_t *)(hello_pci_info.address_bar0 + 0x20)) = 0x80;
return 0;
}
static void hello_pcie_remove(struct pci_dev *dev)
{
// disable irq for finishing factorial computation
*((uint32_t *)(hello_pci_info.address_bar0 + 0x20)) = 0x01;
free_irq(dev->irq, &hello_pci_info);
pci_iounmap(dev, hello_pci_info.address_bar0);
pci_disable_device(dev);
}
static struct pci_driver hello_pci_driver = {
.name = "hello_pcie",
.id_table = ids,
.probe = hello_pcie_probe,
.remove = hello_pcie_remove,
};
static int __init hello_pci_init(void)
{
int ret = pci_register_driver(&hello_pci_driver);
if(hello_pci_info.dev == NULL){
printk("hello_pci: probe pcie device failed!\n");
return ret;
}
/* 1、Request device number */
ret = alloc_chrdev_region(&hello_pci_info.dev_id, 0, 1, "hello_pcie");
/* 2、Initial char_dev */
hello_pci_info.char_dev.owner = THIS_MODULE;
cdev_init(&hello_pci_info.char_dev, &hello_pcie_fops);
/* 3、add char_dev */
cdev_add(&hello_pci_info.char_dev, hello_pci_info.dev_id, 1);
/* 4、create class */
hello_pci_info.class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "hello_pcie");
if (IS_ERR(hello_pci_info.class)) {
return PTR_ERR(hello_pci_info.class);
}
/* 5、create device */
hello_pci_info.device = device_create(hello_pci_info.class, NULL, hello_pci_info.dev_id, NULL, "hello_pcie");
if (IS_ERR(hello_pci_info.device)) {
return PTR_ERR(hello_pci_info.device);
}
return ret;
}
static void __exit hello_pci_exit(void)
{
if(hello_pci_info.dev != NULL) {
cdev_del(&hello_pci_info.char_dev); /* del cdev */
unregister_chrdev_region(hello_pci_info.dev_id, 1); /* unregister device number */
device_destroy(hello_pci_info.class, hello_pci_info.dev_id);
class_destroy(hello_pci_info.class);
}
pci_unregister_driver(&hello_pci_driver);
}
module_init(hello_pci_init);
module_exit(hello_pci_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
MODULE_INFO(intree, "Y");
四、编写用户程序
编写用户测试程序testapp.c如下:
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdint.h"
#include "unistd.h"
#include "sys/types.h"
#include "sys/stat.h"
#include "fcntl.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
#include "string.h"
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int fd, retvalue;
char *filename = "/dev/hello_pcie";
uint32_t data_val = 6;
int read_val;
/* 打开驱动设备文件 */
fd = open(filename, O_RDWR);
if(fd < 0){
printf("file %s open failed!\n", filename);
return -1;
}
/* 向/dev/hello_pcie文件写入数据 */
retvalue = write(fd, &data_val, sizeof(int));
if(retvalue < 0){
printf("Open %s Failed!\n", filename);
close(fd);
return -1;
}
read(fd, &read_val, sizeof(int));
printf("factorial computation result : %0d \n", read_val);
retvalue = close(fd); /* 关闭文件 */
if(retvalue < 0){
printf("file %s close failed!\r\n", filename);
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
五、运行测试
编译加载驱动,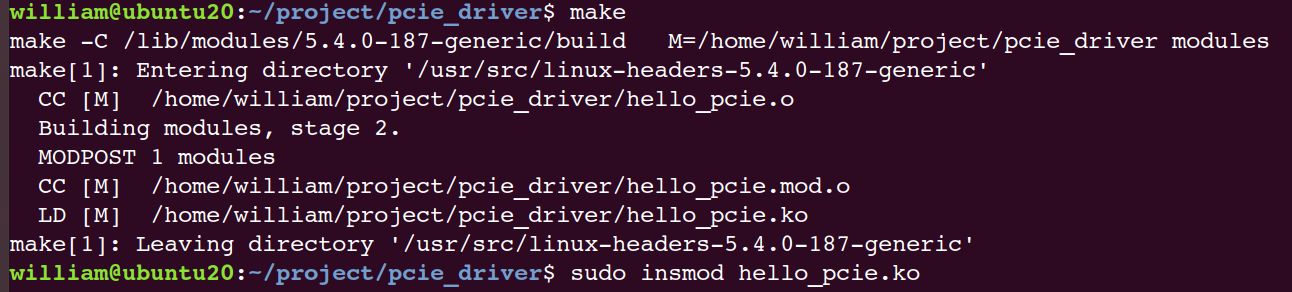
使用如下命令编译测试程序:
gcc testapp.c
然后运行测试程序,我们可以看到计算得到的阶乘结果为720,即6*5*4*3*2*1=720,符合预期结果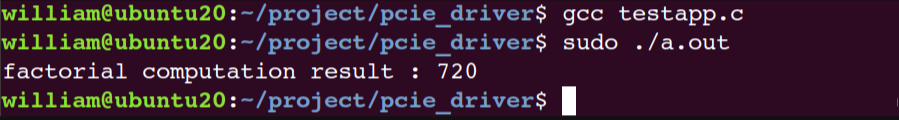
 一个最简单的LINUX-PCIE设备驱动
一个最简单的LINUX-PCIE设备驱动





